I assume you already have an Amazon RDS DB instance. If not, just create a free-tier one.
Then, click on your DB instance → Configuration → Manage in Secrets Manager. Here, you will find your Secret Name.
You will need this in your Laravel service later.
But first, you need to create an IAM Role, so your EC2 instance can connect to the database easily.
At the top right corner, you should see your AWS username. Click on it, and in the dropdown menu, click Security Credentials → Roles → Create Role → AWS Service → Use case: EC2. Then, select the SecretsManagerReadWrite policy (you can customize permissions later to control what your EC2 instance can and cannot access).
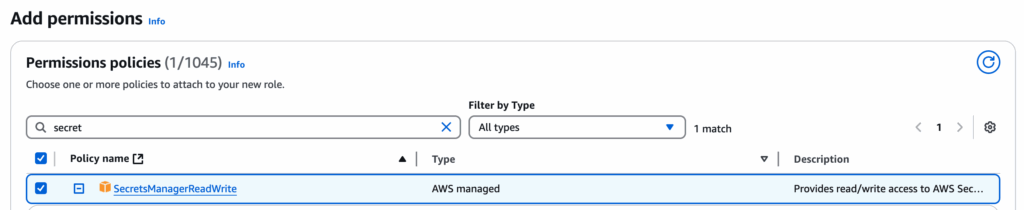
Give the role a name, for example: EC2-SecretManager-Role.
That’s it!
Now your EC2 instance can communicate with Secrets Manager.
(Of course, you could make it even more secure by allowing access to only specific databases for specific instances — you can fine-tune this with IAM policies.)
First, you’ll need to install the AWS SDK
composer require aws/aws-sdk-phpCode language: JavaScript (javascript)
Now, create a service class in your Laravel application at app/Services/AWSSecretsManager.php
<?php
namespace App\Services;
use Aws\Exception\AwsException;
use Aws\SecretsManager\SecretsManagerClient;
class AWSSecretsManagerService
{
public function getSecret($secretName)
{
$client = new SecretsManagerClient([
'version' => 'latest',
'region' => 'eu-central-1'
]);
try {
$result = $client->getSecretValue([
'SecretId' => $secretName,
]);
} catch (AwsException $e) {
throw $e;
}
return json_decode($result['SecretString'], true);
}
}Code language: PHP (php)This function connects to AWS Secrets Manager every time your application connects to the database, so you no longer need to store DB credentials in your .env file.
The final step: you should add your database configuration in .env, but fetch the username and password dynamically from Secrets Manager.
When you click on your database instance in AWS, you’ll find:

- Endpoint → use it as your
DB_HOST - Database Name → use it as your
DB_DATABASE
The magic happens in config/database.php
if (env('APP_ENV') === 'production') {
$secretsManager = app(\App\Services\AWSSecretsManagerService::class);
$secrets = $secretsManager->getSecret('your-secret-name-from-the-beginning-of-the-post');
}Code language: PHP (php)'mysql' => [
'username' => env('APP_ENV') === 'production' ? $secrets['username'] : env('DB_USERNAME', 'root'),
'password' => env('APP_ENV') === 'production' ? $secrets['password'] : env('DB_PASSWORD', ''),
],Code language: PHP (php)
Tadaaa! 🎉
Now you have a secure AWS EC2 → AWS RDS connection in Laravel without hardcoding your database credentials!